Remote sensing
The United Nations in
their annex Principles Relating to Remote Sensing of the Earth from Space
say that:
"The term Remote
Sensing means the sensing of the Earth's surface from space by making use
of the properties of electromagnetic waves emitted, reflected or diffracted
by the sensed objects, for the purpose of improving natural resources management,
land use and the protection of the environment."
For
instance, film photography is a form of optical remote sensing that uses photosensitive
chemicals to form an image, while radar is a type of remote sensing that uses
reflected radio energy to determine the distance, shape, and texture of objects.
Satellite
imaging systems normally use electronic sensors instead of film and can broadcast
the image data back for real time viewing and analysis.
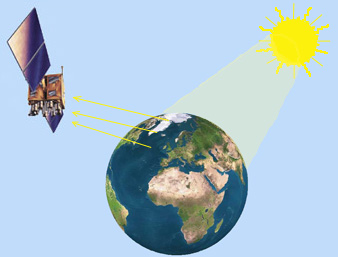
Eyes, ears, film, and most satellite systems are considered "passive"
systems since they rely upon other sources of energy (sunlight, temperature,
etc.) to produce their sensory reaction.
Example
of a passive sensor
Remote
sensing is the science of gathering information from a distance. The human eye
is a form of optical remote sensor, as the ear is a form of acoustical remote
sensor. Remote sensing consists of a wide variety of technologies